Adam Brzeski, Jan Cychnerski, Tomasz Dziubich, Paweł Kaczmarek
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.903.4195&rep=rep1&type=pdf#page=153
Computer driven medical image recognition may support medical doctors in the diagnosis process, but requires high dependability considering potential consequences of incorrect results. The paper presents a system that improves dependability of medical image recognition by integration of results from redundant components.
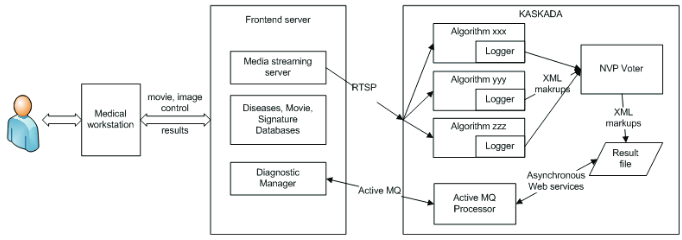
The components implement alternative recognition algorithms of diseases in the field of gastrointestinal endoscopy. In our solution, we consider both algorithms that detect a single disease and algorithms that detect many diseases, in which case results from different algorithms are partially overlapping. The information is processed using the N-version programming (NVP) pattern to vote the final result. The solution adapts the standard NVP pattern to the specifics of the application area covering issues such as: managing diseases recognized by components, components reliability and data streaming.
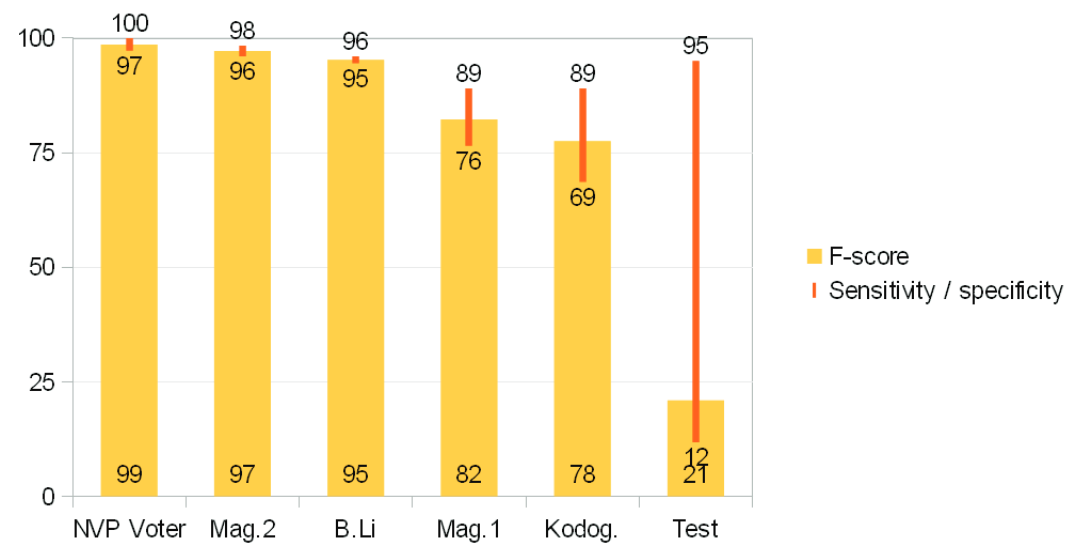
We maintain a catalog of known integrated components together with their reliability rating. The solution is a part of a complex service deployed and run in the KASKADA environment that is a framework for processing of computational intensive data in the streaming model. The KASKADA environment leverages the clustering architecture of supercomputer centers to allocate computational tasks to available computing nodes. Tests and results of exemplary disease recognition performed in the environment are presented.
Information Systems Architecture and Technology: System Analysis Approach to Design, Control and Decision Support. Oficyna Wydawnicza PWr, 2012